Keyword: シンプレックス法, 関数の最小化
概要
本サンプルはシンプレックス法による関数の最小化を行うC言語によるサンプルプログラムです。 本サンプルはNelder-Meadシンプレックス法により以下に示される関数の最小値を求めて出力します。本サンプルではx1とx2の初期値を(−1.0,1.0)として計算しています。
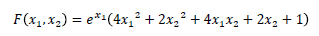
※本サンプルはnAG Cライブラリに含まれる関数 nag_opt_simplex_easy() のExampleコードです。本サンプル及び関数の詳細情報は nag_opt_simplex_easy のマニュアルページをご参照ください。
ご相談やお問い合わせはこちらまで
出力結果
(本関数の詳細はnag_opt_simplex_easy のマニュアルページを参照)| この出力例をダウンロード |
nag_opt_simplex_easy (e04cbc) Example Program Results (User-supplied callback funct, first invocation.) (User-supplied callback monit, first invocation.) The final function value is 0.0000 at the point 0.5000 -0.9999
- 2行目に最小の関数値が出力されています。
- 3行目に最小の関数値に対応するxの値が出力されています。
ソースコード
(本関数の詳細はnag_opt_simplex_easy のマニュアルページを参照)
※本サンプルソースコードはnAG数値計算ライブラリ(Windows, Linux, MAC等に対応)の関数を呼び出します。
サンプルのコンパイル及び実行方法
| このソースコードをダウンロード |
/* nag_opt_simplex_easy (e04cbc) Example Program.
*
* CLL6I261D/CLL6I261DL Version.
*
* Copyright 2017 Numerical Algorithms Group.
*
* Mark 26.1, 2017.
*/
#include <nag.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <nag_stdlib.h>
#include <nage04.h>
#include <nagx02.h>
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C"
{
#endif
static void nAG_CALL funct(const Integer n, const double *xc, double *fc,
Nag_Comm *comm);
static void nAG_CALL monit(const double fmin, const double fmax,
const double sim[], const Integer n,
const Integer ncall, const double serror,
const double vratio, Nag_Comm *comm);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
int main(void)
{
/* Scalars */
double f, tolf, tolx;
Integer exit_status, i, monitoring, maxcal = 100, n = 2;
NagError fail;
/* Arrays */
static double ruser[2] = { -1.0, -1.0 };
double *x = 0;
Nag_Comm comm;
exit_status = 0;
INIT_FAIL(fail);
printf("nag_opt_simplex_easy (e04cbc) Example Program Results\n");
/* For communication with user-supplied functions: */
comm.user = ruser;
/* Allocate memory */
if (!(x = nAG_ALLOC(n, double)))
{
printf("Allocation failure\n");
exit_status = -1;
goto END;
}
/* Set monitoring to a nonzero value to obtain monitoring information */
monitoring = 0;
comm.p = (Pointer) &monitoring;
/* Starting values */
x[0] = -1.0;
x[1] = 1.0;
tolf = sqrt(nag_machine_precision);
tolx = sqrt(tolf);
nag_opt_simplex_easy(n, x, &f, tolf, tolx, funct, monit, maxcal, &comm,
&fail);
if (fail.code != NE_NOERROR) {
printf("Error from nag_opt_simplex_easy (e04cbc).\n%s\n", fail.message);
exit_status = 1;
goto END;
}
printf("The final function value is %12.4f\n", f);
printf("at the point");
for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
printf(" %12.4f", x[i - 1]);
}
printf("\n");
END:
nAG_FREE(x);
return exit_status;
}
static void nAG_CALL funct(const Integer n, const double *xc, double *fc,
Nag_Comm *comm)
{
if (comm->user[0] == -1.0) {
printf("(User-supplied callback funct, first invocation.)\n");
comm->user[0] = 0.0;
}
*fc = exp(xc[0]) * (4.0 * xc[0] * (xc[0] + xc[1]) +
2.0 * xc[1] * (xc[1] + 1.0) + 1.0);
}
static void nAG_CALL monit(const double fmin, const double fmax,
const double sim[], const Integer n,
const Integer ncall, const double serror,
const double vratio, Nag_Comm *comm)
{
#define SIM(I, J) sim[(J-1)*(n+1) + (I-1)]
Integer i, j;
Integer monitoring = *(Integer *) comm->p;
if (comm->user[1] == -1.0) {
printf("(User-supplied callback monit, first invocation.)\n");
comm->user[1] = 0.0;
}
if (monitoring != 0) {
printf("\nThere have been %5ld function calls\n", ncall);
printf("The smallest function value is %10.4f\n", fmin);
printf("\nThe simplex is\n");
for (i = 1; i <= n + 1; ++i) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
printf(" %13.4e", SIM(i, j));
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\nThe standard deviation in function values at the"
" vertices of the simplex is %10.4f\n", serror);
printf("The linearized volume ratio of the current simplex"
" to the starting one is %10.4f\n", vratio);
}
}
